
 Caste and Democracy
Caste and DemocracySri Aurobindo
Bande Mataram
Calcutta, September 21st, 1907
Part Four. Bande Mataram under the Editorship of of Sri Aurobindo (28 May – 22 December 1907)

 Caste and Democracy
Caste and Democracy
We fear our correspondent who has criticised on another page the consistency of our views on caste, has hardly taken any trouble to understand the real drift of our articles.
His attitude seems to be that we must be either entirely for caste as it at present exists or entirely against the institution and condemn it root and branch in the style of the ordinary unthinking social reformer.
Because on the one hand we protested against the ignorant abuse of the institution often indulged in simply because it is different in form and spirit from European institutions, and on the other hand emphasized1 the perversions of its form and spirit and the necessity of its transformation in the pure spirit of Hinduism, our correspondent imagines that we are inconsistent and guilty of adopting successively two different and incompatible attitudes.
Our position is perfectly clear and straightforward.
Caste was originally an arrangement for the distribution of functions in society, just as much as class in Europe, but the principle on which the distribution was based in India was peculiar to this country.
The civilisation of Europe has always been preponderatingly material and the division of classes was material in its principles and material in its objects, but our civilisation has always been preponderatingly spiritual and moral, and caste division in India had a spiritual object and a spiritual and moral basis.
The division of classes in Europe had its root in a distribution of powers and rights and developed and still develops through a struggle of conflicting interests; its aim was merely the organisation of society for its own sake and mainly indeed for its economic convenience.
The division of castes in India was conceived as a distribution of duties.
A man’s caste depended on his dharma, his 
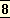
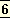
 spiritual, moral and practical duties, and his dharma depended on his swabhava, his temperament and inborn nature.
A Brahmin was a Brahmin not by mere birth, but because he discharged the duty of preserving the spiritual and intellectual elevation of the race, and he had to cultivate the spiritual temperament and acquire the spiritual training which could alone qualify him for the task.
The Kshatriya was a Kshatriya not merely because he was the son of warriors and princes, but because he discharged the duty of protecting the country and preserving the high courage and manhood of the nation, and he had to cultivate the princely temperament and acquire the strong and lofty Samurai training which alone fitted him for his duties.
So it was with the Vaishya whose function was to amass wealth for the race and the Sudra who discharged the humbler duties of service without which the other castes could not perform their share of labour for the common good.
This was what we meant when we said that caste was a socialistic institution.
No doubt there was a gradation of social respect which placed the function of the Brahmin at the summit and the function of the Sudra at the base, but this inequality was accidental, external, vyavaharika.
Essentially there was, between the devout Brahmin and the devout Sudra, no inequality in the single Virat Purusha of which each was a necessary part.
Chokha Mela, the Maratha Pariah, became the guru of Brahmins proud of their caste purity; the Chandala taught Shankaracharya: for the Brahman was revealed in the body of the Pariah and in the Chandala there was the utter presence of Shiva the Almighty.
Heredity entered into caste divisions, and in the light of the conclusions of modern knowledge who shall say erroneously?
But it entered into it as a subordinate element.
For Hindu civilisation being spiritual based its institutions on spiritual and moral foundations and subordinated the material elements and material considerations.
Caste therefore was not only an institution which ought to be immune from the cheap second-hand denunciations so long in fashion, but a supreme necessity without which Hindu civilisation could not have developed its distinctive character or worked out its unique mission.
spiritual, moral and practical duties, and his dharma depended on his swabhava, his temperament and inborn nature.
A Brahmin was a Brahmin not by mere birth, but because he discharged the duty of preserving the spiritual and intellectual elevation of the race, and he had to cultivate the spiritual temperament and acquire the spiritual training which could alone qualify him for the task.
The Kshatriya was a Kshatriya not merely because he was the son of warriors and princes, but because he discharged the duty of protecting the country and preserving the high courage and manhood of the nation, and he had to cultivate the princely temperament and acquire the strong and lofty Samurai training which alone fitted him for his duties.
So it was with the Vaishya whose function was to amass wealth for the race and the Sudra who discharged the humbler duties of service without which the other castes could not perform their share of labour for the common good.
This was what we meant when we said that caste was a socialistic institution.
No doubt there was a gradation of social respect which placed the function of the Brahmin at the summit and the function of the Sudra at the base, but this inequality was accidental, external, vyavaharika.
Essentially there was, between the devout Brahmin and the devout Sudra, no inequality in the single Virat Purusha of which each was a necessary part.
Chokha Mela, the Maratha Pariah, became the guru of Brahmins proud of their caste purity; the Chandala taught Shankaracharya: for the Brahman was revealed in the body of the Pariah and in the Chandala there was the utter presence of Shiva the Almighty.
Heredity entered into caste divisions, and in the light of the conclusions of modern knowledge who shall say erroneously?
But it entered into it as a subordinate element.
For Hindu civilisation being spiritual based its institutions on spiritual and moral foundations and subordinated the material elements and material considerations.
Caste therefore was not only an institution which ought to be immune from the cheap second-hand denunciations so long in fashion, but a supreme necessity without which Hindu civilisation could not have developed its distinctive character or worked out its unique mission.
But to recognise this is not to debar ourselves from pointing 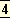
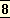
 out its later perversions and desiring its transformation.
It is the nature of human institutions to degenerate, to lose their vitality, and decay, and the first sign of decay is the loss of flexibility and oblivion of the essential spirit in which they were conceived.
The spirit is permanent, the body changes; and a body which refuses to change must die.
The spirit expresses itself in many ways while itself remaining essentially the same, but the body must change to suit its changing environments if it wishes to live.
There is no doubt that the institution of caste degenerated.
It ceased to be determined by spiritual qualifications which, once essential, have now come to be subordinate and even immaterial and is determined by the purely material tests of occupation and birth.
By this change it has set itself against the fundamental tendency of Hinduism which is to insist on the spiritual and subordinate the material and thus lost most of its meaning.
The spirit of caste arrogance, exclusiveness and superiority came to dominate it instead of the spirit of duty, and the change weakened the nation and helped to reduce us to our present condition.
It is these perversions which we wish to see set right.
The institution must transform itself so as to fulfil its essential and permanent object under the changed conditions of modern times.
If it refuses to change, it will become a mere social survival and crumble to pieces.
If it transforms itself, it will yet play a great part in the fulfilment of civilisation.
out its later perversions and desiring its transformation.
It is the nature of human institutions to degenerate, to lose their vitality, and decay, and the first sign of decay is the loss of flexibility and oblivion of the essential spirit in which they were conceived.
The spirit is permanent, the body changes; and a body which refuses to change must die.
The spirit expresses itself in many ways while itself remaining essentially the same, but the body must change to suit its changing environments if it wishes to live.
There is no doubt that the institution of caste degenerated.
It ceased to be determined by spiritual qualifications which, once essential, have now come to be subordinate and even immaterial and is determined by the purely material tests of occupation and birth.
By this change it has set itself against the fundamental tendency of Hinduism which is to insist on the spiritual and subordinate the material and thus lost most of its meaning.
The spirit of caste arrogance, exclusiveness and superiority came to dominate it instead of the spirit of duty, and the change weakened the nation and helped to reduce us to our present condition.
It is these perversions which we wish to see set right.
The institution must transform itself so as to fulfil its essential and permanent object under the changed conditions of modern times.
If it refuses to change, it will become a mere social survival and crumble to pieces.
If it transforms itself, it will yet play a great part in the fulfilment of civilisation.
Our correspondent accuses us of attempting to corrupt society with the intrusion of the European idea of Socialism.
Socialism is not an European idea, it is essentially Asiatic and especially Indian.
What is called Socialism in Europe, is the old Asiatic attempt to effect a permanent solution of the economic problem of society which will give man leisure and peace to develop undisturbed his higher self.
Without Socialism democracy would remain a tendency that never reached its fulfilment, a rule of the masses by a small aristocratic or monied class with the consent and votes of the masses, or a tyranny of the artisan classes over the rest.
Socialistic democracy is the only true democracy, for without it we cannot get the equalised and harmonised distribution of functions, each part of the community existing for 
 the good of all and not struggling for its own separate interests, which will give humanity as a whole the necessary conditions in which it can turn its best energies to its higher development.
To realise those conditions is also the aim of Hindu civilisation and the original intention of caste.
The fulfilment of Hinduism is the fulfilment of the highest tendencies of human civilisation and it must include in its sweep the most vital impulses of modern life.
It will include democracy and Socialism also, purifying them, raising them above the excessive stress on the economic adjustments which are the means, and teaching them to fix their eyes more constantly and clearly on the moral, intellectual and spiritual perfection of mankind which is the end.
the good of all and not struggling for its own separate interests, which will give humanity as a whole the necessary conditions in which it can turn its best energies to its higher development.
To realise those conditions is also the aim of Hindu civilisation and the original intention of caste.
The fulfilment of Hinduism is the fulfilment of the highest tendencies of human civilisation and it must include in its sweep the most vital impulses of modern life.
It will include democracy and Socialism also, purifying them, raising them above the excessive stress on the economic adjustments which are the means, and teaching them to fix their eyes more constantly and clearly on the moral, intellectual and spiritual perfection of mankind which is the end.
Earlier edition of this work: Sri Aurobindo Birth Century Library: Set in 30 volumes.- Volume 1.- Bande Mataram: Early Political Writings. 1890 - May 1908.- Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 1973.- 920 p.
1 1973 ed. SABCL, vol.1: emphasised