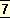

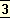
 Curzonism for the University
Curzonism for the UniversitySri Aurobindo
Bande Mataram
Early Political Writings. 1890 — May 1908
Bande Mataram. May 8, 1907
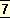

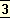
 Curzonism for the University
Curzonism for the University
At last the brahmāstra which Lord Curzon forged for the stifling of patriotism through the instrumentality of the University, is to be utilised, and utilised to its full capacity. We all remember the particular skirmish in the first Swadeshi struggle in which Sir Bampfylde Fuller fell. Sir Bampfylde insisted on the disaffiliation of the Serajgunge Schools because the teachers and students were publicly taking part in politics. Lord Minto's Government refused to support him in this action because it was inadvisable, having regard to the troubled nature of the times, and Sir Bampfylde had to resign. Whatever stronger motives were behind Lord Minto's action, this was the ostensible occasion for a resignation which practically amounted to a dismissal. Now we find the same Government and the same Lord Minto out-fullering Fuller and threatening in much more troubled times against all Government or aided or affiliated Colleges and Schools the action which Sir Bampfylde contemplated against only two.
The circular letter issued to the local Governments “with the object of protecting Higher Education in India” from any connection with politics, is an awkward and clumsily worded document such as we would not have expected from the pen of Sir H. Risley, but it manages to make its object and methods pretty clear.
The object is to put a stop to the system of National Volunteers which is growing up throughout Bengal, to use the Universities as an instrument for stifling the growth of political life and incidentally to prevent men of ability and influence in the educational line from becoming a political power.
This is how Lord Minto, presumably with the approval of Mr. John Morley, proposes to bring about these objects.
The objects of their benevolent and high-minded attention are divided into four classes, schoolboys, college students, school masters, professors, and for each a scientifically varied treatment is carefully prescribed. 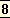

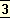

For students in high schools, “In the interest of the boys themselves, it is clearly undesirable that they should be distracted from their work by attending political meetings or engaging in any form of political agitation.
In the event of such misconduct being persisted in and encouraged or permitted by masters or managing authorities, the offending school can after due warning be dealt with – (a) by the local Government, which has the power of withdrawing any grant-in-aid and of withholding the privilege of competing for scholarships and of receiving scholarship-holders; (b) by the University, which can withdraw recognition from the school, the effect of which is to prevent it from sending up pupils as candidates for matriculation examination.” Students in high school1 are therefore to be debarred from all political education and brought up on an exclusive diet of Lee Warner and Empire Day.
Attending political meetings, outside school hours mind you, and, it may be, with the full consent of the guardians, is to be reckoned as misconduct coming within the scope of school discipline.
It is to be punished by the disciplining, that is to say, the flogging or expulsion of the boys.
But what if the teachers or the managing authorities remember that they are men and not dogs who for a little food from the Government are ready to do its will just or unjust?
What if they decline to do the Government's dirty work for it?
Then the local magistrate appears on the scene and takes away the grant-in-aid and the privilege of competing for scholarships and of receiving scholarship-holders.
But supposing there should still be found a Vidyasagar or two who would contemptuously spurn these bribes and prefer to keep his manhood?
For that also this provident circular has provided.
The school can be refused recognition, a refusal which will mean exclusion of its students from a college education.
For this purpose the local Government will report to the University “which alone is legally competent to inflict the requisite penalty”.
But if this sole legal authority should decline to act on the report of the local Government?
Then, it appears, there is another sole authority which is legally or illegally competent, the Government itself.
The report is to be understood not as a report but as an order, and if it is disobeyed, the University “would fail to carry out the educational trust with which the law 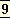

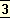
 has invested it, and it would be the duty of the Government to intervene”.
has invested it, and it would be the duty of the Government to intervene”.
The next class is composed of university students. In their case the Government is not prepared to punish them, as a general rule, for merely attending political meetings. We take it that, in special cases, e.g., if it were a meeting addressed by Srijut Bepin2 Chandra Pal or Syed Haldar3 Reza or Mr. Tilak, they will not be punished. But if they take an active part in the meeting, then the need for discipline will begin. Any action which will bring undesirable notoriety upon their college, will be sufficient ground for Government interference. Picketing is of course forbidden to the student and so is open violence – such for instance as the defence of his father's house, person and property from Mahomedan Goondas or of the chastity of his wife, sister or mother from violation by political hooligans.
The schoolmaster is mercifully treated.
He is graciously conceded the right of having his own opinions and even of expressing them within limits set by the alien bureaucracy.
“If, therefore, the public utterances of a schoolmaster are of such a character as to endanger the orderly development of the boys under his charge by introducing into their immature minds doctrines subversive of their respect for authority and calculated to impair their usefulness as citizens and to hinder their advancement in after life, his proceedings must be held to constitute a dereliction of duty, and may properly be visited with disciplinary action.” In plain unofficial English the schoolmaster will be allowed to teach loyalty and subservience, but if he teaches patriotism, he must be suspended, degraded or dismissed.
If he takes his pupils or encourages them to go to political meetings,– barring celebrations of the Empire Day,– he will, of course, be dismissed at once.
Finally, the College Professors, men like Srijut4 Surendranath Banerji, Aswini Kumar Dutt5, Krishna Kumar Mitra, are not to be altogether gagged, but their hands are to be bound.
“If he diverts his students' minds to political agitation”, as Srijut Surendranath has done for decades; “if he encourages them to attend political meetings or personally” conducts them to such meetings,– this is obviously aimed at Srijut Krishna Kumar Mitra and the Anti-Circular 
 Society – “or if he adopts a line of action which disturbs and disorganises the life and work of the College at which he is employed”,– whatever this portentous phrase may mean,– the College is to be disaffiliated or the offender expelled.
Society – “or if he adopts a line of action which disturbs and disorganises the life and work of the College at which he is employed”,– whatever this portentous phrase may mean,– the College is to be disaffiliated or the offender expelled.
This ukase out-Russias Russia. Not even in Russia have such systematically drastic measures been taken to discourage political life and patriotic activity among the young. Not even the omnipotent Tsar has dared to issue an ukase so arbitrary, oppressive and inquisitorial. It means that no self-respecting patriot will in future enter or remain in the Government educational service in any position of responsibility; or if he remains, he will not be allowed to remain long. It means that the position of private schools and colleges will become unbearable and they will be compelled to break off connection with the Government University. It means, if there is a grain of self-respect left in the country, that the Government University will perish and a National University be developed. And for this reason we welcome the circular and hope that its provisions will be stringently enforced.
Later edition of this work: The Complete Works of Sri Aurobindo.- Set in 37 volumes.- Volumes 6-7.- Bande Mataram: Political Writings and Speeches. 1890–1908 .- Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 2002.- 1182 p.
1 2002 ed. CWSA, vol.6-7: schools
2 2002 ed. CWSA, vol.6-7: Bipin
3 2002 ed. CWSA, vol.6-7: Haidar
4 2002 ed. CWSA, vol.6-7: Srijuts
5 2002 ed. CWSA, vol.6-7: Dutta