Sri Aurobindo
Letters of Sri Aurobindo
Volume 2. 1934 — 1935
No, certainly not – an Avatar is not at all bound to be a 
 spiritual prophet – he is never in fact merely a prophet, he is a realiser, an establisher – not of outward things only, though he does realise something in the outward also, but, as I have said, of something essential and radical needed for the terrestrial evolution which is the evolution of the embodied spirit through successive stages towards the Divine. It was not at all Rama’s business to establish the spiritual stage of that evolution – so he did not at all concern himself with that. His business was to destroy Ravana and to establish the Ramarajya – in other words, to fix for the future the possibility of an order proper to the sattwic civilised human being who governs his life by the reason, the finer emotions, morality, or at least moral ideals, such as truth, obedience, co-operation and harmony, the sense of honour, the sense of domestic and public order, to establish this in a world still occupied by anarchic forces, the Animal Mind and the powers of the vital Ego making its own satisfaction the rule of life, in other words, the Vānara and the Rākṣasa1. This is the meaning of Rama and his life-work and it is according as he fulfilled it or not that he must be judged as Avatar or no Avatar. It was not his business to play the comedy of the chivalrous Kṣatriya2 with the formidable brute beast that was Bāli, it was his business to kill him and get the Animal Mind under his control. It was his business to be not necessarily a perfect, but a largely representative sattwic Man, a faithful husband and a lover, a loving and obedient son, a tender and perfect brother, father, friend – he is friend of all kinds of people, friend of the outcast Guhaka, friend of the Animal leaders, Sugriva, Hanuman, friend of the vulture Jatayu, friend even of the Rākṣasa Vibhishana. All that he was in a brilliant, striking but above all spontaneous and inevitable way, not with a forcing of this note or that like Harishchandra3 or Shivi4, but with a certain harmonious completeness. But most of all, it was his business to typify and establish the things on which the social idea and its stability depend, truth and honour, the sense of the Dharma, public spirit and the sense of order. To the first, to truth and honour, much more than to his filial love and
spiritual prophet – he is never in fact merely a prophet, he is a realiser, an establisher – not of outward things only, though he does realise something in the outward also, but, as I have said, of something essential and radical needed for the terrestrial evolution which is the evolution of the embodied spirit through successive stages towards the Divine. It was not at all Rama’s business to establish the spiritual stage of that evolution – so he did not at all concern himself with that. His business was to destroy Ravana and to establish the Ramarajya – in other words, to fix for the future the possibility of an order proper to the sattwic civilised human being who governs his life by the reason, the finer emotions, morality, or at least moral ideals, such as truth, obedience, co-operation and harmony, the sense of honour, the sense of domestic and public order, to establish this in a world still occupied by anarchic forces, the Animal Mind and the powers of the vital Ego making its own satisfaction the rule of life, in other words, the Vānara and the Rākṣasa1. This is the meaning of Rama and his life-work and it is according as he fulfilled it or not that he must be judged as Avatar or no Avatar. It was not his business to play the comedy of the chivalrous Kṣatriya2 with the formidable brute beast that was Bāli, it was his business to kill him and get the Animal Mind under his control. It was his business to be not necessarily a perfect, but a largely representative sattwic Man, a faithful husband and a lover, a loving and obedient son, a tender and perfect brother, father, friend – he is friend of all kinds of people, friend of the outcast Guhaka, friend of the Animal leaders, Sugriva, Hanuman, friend of the vulture Jatayu, friend even of the Rākṣasa Vibhishana. All that he was in a brilliant, striking but above all spontaneous and inevitable way, not with a forcing of this note or that like Harishchandra3 or Shivi4, but with a certain harmonious completeness. But most of all, it was his business to typify and establish the things on which the social idea and its stability depend, truth and honour, the sense of the Dharma, public spirit and the sense of order. To the first, to truth and honour, much more than to his filial love and 
 obedience to his father – though to that also – he sacrificed his personal rights as the elect of the King and the assembly and fourteen of the best years of his life and went into exile in the forests. To his public spirit and his sense of public order (the great and supreme civic virtue in the eyes of the ancient Indians, Greeks, Romans, for at that time the maintenance of the ordered community, not the separate development and satisfaction of the individual was the pressing need of the human evolution) he sacrificed his own happiness and domestic life and the happiness of Sita. In that he was at one with the moral sense of all the antique races, though at variance with the later romantic individualistic sentimental morality of the modern man who can afford to have that less stern morality just because the ancients sacrificed the individual in order to make the world safe for the spirit of social order. Finally, it was Rama’s business to make the world safe for the ideal of the sattwic human being by destroying the sovereignty of Ravana, the Rākṣasa menace. All this he did with such a divine afflatus in his personality and action that his figure has been stamped for more than two millenniums on the mind of Indian culture, and what he stood for has dominated the reason and idealising mind of man in all countries – and in spite of the constant revolt of the human vital, is likely to continue to do so until a greater Ideal arises. And you say in spite of all these that he was no Avatar? If you like – but at any rate he stands among the few greatest of the great Vibhūtis. You may dethrone him now – for man is no longer satisfied with the sattwic ideal and is seeking for something more – but his work and meaning remain stamped on the past of the earth’s evolving race.
obedience to his father – though to that also – he sacrificed his personal rights as the elect of the King and the assembly and fourteen of the best years of his life and went into exile in the forests. To his public spirit and his sense of public order (the great and supreme civic virtue in the eyes of the ancient Indians, Greeks, Romans, for at that time the maintenance of the ordered community, not the separate development and satisfaction of the individual was the pressing need of the human evolution) he sacrificed his own happiness and domestic life and the happiness of Sita. In that he was at one with the moral sense of all the antique races, though at variance with the later romantic individualistic sentimental morality of the modern man who can afford to have that less stern morality just because the ancients sacrificed the individual in order to make the world safe for the spirit of social order. Finally, it was Rama’s business to make the world safe for the ideal of the sattwic human being by destroying the sovereignty of Ravana, the Rākṣasa menace. All this he did with such a divine afflatus in his personality and action that his figure has been stamped for more than two millenniums on the mind of Indian culture, and what he stood for has dominated the reason and idealising mind of man in all countries – and in spite of the constant revolt of the human vital, is likely to continue to do so until a greater Ideal arises. And you say in spite of all these that he was no Avatar? If you like – but at any rate he stands among the few greatest of the great Vibhūtis. You may dethrone him now – for man is no longer satisfied with the sattwic ideal and is seeking for something more – but his work and meaning remain stamped on the past of the earth’s evolving race.
When I spoke of the gap that would be left by his absence, I did not mean a gap among the prophets and intellectuals, but a gap in the scheme of Avatarhood – there was somebody who was the Avatar of the sattwic Human as Krishna was the Avatar of the overmental Superhuman – I see no one but Rama who can fill the place. Spiritual teachers and prophets (as also intellectuals, scientists, artists, poets, etc.) – these are 
 at the greatest Vibhūtis, but they are not Avatars. For at that rate all religious founders would be Avatars – Joseph Smith (I think that is his name) of the Mormons, St. Francis of Assisi, Calvin, Loyola and a host of others as well as Christ, Chaitanya or Ramakrishna.
at the greatest Vibhūtis, but they are not Avatars. For at that rate all religious founders would be Avatars – Joseph Smith (I think that is his name) of the Mormons, St. Francis of Assisi, Calvin, Loyola and a host of others as well as Christ, Chaitanya or Ramakrishna.
For faith, miracles, Bejoy Goswami5, another occasion. I wanted to say this much more about Rama – which is still only a hint and is not the thing I was going to write about the general principle of the Avatar. Nor, I may add, is it a complete or supreme defence of Rama. For that I would have to write about what the story of the Ramayana meant, appreciate Valmiki’s presentation of his chief characters (they are none of them copy-book examples, but great men and women with the defects and merits of human nature, as all men even the greatest are), and show also how the Godhead, which was behind the frontal and instrumental personality we call Rama, worked out every incident of his life as a necessary step in what had to be done. As to the weeping of Rama, I had answered that in my other unfinished letter. You are imposing the colder and harder Nordic ideal on the Southern temperament which regarded the expression of emotions, not its suppression, as a virtue. Witness the weeping and lamentations of Achilles, Ulysses and other Greek, Persian and Indian heroes – the latter especially as lovers.
 spiritual prophet – he is never in fact merely a prophet, he is a realiser, an establisher – not of outward things only, though he does realise something in the outward also, but, as I have said, of something essential and radical needed for the terrestrial evolution which is the evolution of the embodied spirit through successive stages towards the Divine. It was not at all Rama’s business to establish the spiritual stage of that evolution – so he did not at all concern himself with that. His business was to destroy Ravana and to establish the Ramarajya – in other words, to fix for the future the possibility of an order proper to the sattwic civilised human being who governs his life by the reason, the finer emotions, morality, or at least moral ideals, such as truth, obedience, co-operation and harmony, the sense of honour, the sense of domestic and public order, to establish this in a world still occupied by anarchic forces, the Animal Mind and the powers of the vital Ego making its own satisfaction the rule of life, in other words, the Vānara and the Rākṣasa1. This is the meaning of Rama and his life-work and it is according as he fulfilled it or not that he must be judged as Avatar or no Avatar. It was not his business to play the comedy of the chivalrous Kṣatriya2 with the formidable brute beast that was Bāli, it was his business to kill him and get the Animal Mind under his control. It was his business to be not necessarily a perfect, but a largely representative sattwic Man, a faithful husband and a lover, a loving and obedient son, a tender and perfect brother, father, friend – he is friend of all kinds of people, friend of the outcast Guhaka, friend of the Animal leaders, Sugriva, Hanuman, friend of the vulture Jatayu, friend even of the Rākṣasa Vibhishana. All that he was in a brilliant, striking but above all spontaneous and inevitable way, not with a forcing of this note or that like Harishchandra3 or Shivi4, but with a certain harmonious completeness. But most of all, it was his business to typify and establish the things on which the social idea and its stability depend, truth and honour, the sense of the Dharma, public spirit and the sense of order. To the first, to truth and honour, much more than to his filial love and
spiritual prophet – he is never in fact merely a prophet, he is a realiser, an establisher – not of outward things only, though he does realise something in the outward also, but, as I have said, of something essential and radical needed for the terrestrial evolution which is the evolution of the embodied spirit through successive stages towards the Divine. It was not at all Rama’s business to establish the spiritual stage of that evolution – so he did not at all concern himself with that. His business was to destroy Ravana and to establish the Ramarajya – in other words, to fix for the future the possibility of an order proper to the sattwic civilised human being who governs his life by the reason, the finer emotions, morality, or at least moral ideals, such as truth, obedience, co-operation and harmony, the sense of honour, the sense of domestic and public order, to establish this in a world still occupied by anarchic forces, the Animal Mind and the powers of the vital Ego making its own satisfaction the rule of life, in other words, the Vānara and the Rākṣasa1. This is the meaning of Rama and his life-work and it is according as he fulfilled it or not that he must be judged as Avatar or no Avatar. It was not his business to play the comedy of the chivalrous Kṣatriya2 with the formidable brute beast that was Bāli, it was his business to kill him and get the Animal Mind under his control. It was his business to be not necessarily a perfect, but a largely representative sattwic Man, a faithful husband and a lover, a loving and obedient son, a tender and perfect brother, father, friend – he is friend of all kinds of people, friend of the outcast Guhaka, friend of the Animal leaders, Sugriva, Hanuman, friend of the vulture Jatayu, friend even of the Rākṣasa Vibhishana. All that he was in a brilliant, striking but above all spontaneous and inevitable way, not with a forcing of this note or that like Harishchandra3 or Shivi4, but with a certain harmonious completeness. But most of all, it was his business to typify and establish the things on which the social idea and its stability depend, truth and honour, the sense of the Dharma, public spirit and the sense of order. To the first, to truth and honour, much more than to his filial love and 
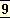
 obedience to his father – though to that also – he sacrificed his personal rights as the elect of the King and the assembly and fourteen of the best years of his life and went into exile in the forests. To his public spirit and his sense of public order (the great and supreme civic virtue in the eyes of the ancient Indians, Greeks, Romans, for at that time the maintenance of the ordered community, not the separate development and satisfaction of the individual was the pressing need of the human evolution) he sacrificed his own happiness and domestic life and the happiness of Sita. In that he was at one with the moral sense of all the antique races, though at variance with the later romantic individualistic sentimental morality of the modern man who can afford to have that less stern morality just because the ancients sacrificed the individual in order to make the world safe for the spirit of social order. Finally, it was Rama’s business to make the world safe for the ideal of the sattwic human being by destroying the sovereignty of Ravana, the Rākṣasa menace. All this he did with such a divine afflatus in his personality and action that his figure has been stamped for more than two millenniums on the mind of Indian culture, and what he stood for has dominated the reason and idealising mind of man in all countries – and in spite of the constant revolt of the human vital, is likely to continue to do so until a greater Ideal arises. And you say in spite of all these that he was no Avatar? If you like – but at any rate he stands among the few greatest of the great Vibhūtis. You may dethrone him now – for man is no longer satisfied with the sattwic ideal and is seeking for something more – but his work and meaning remain stamped on the past of the earth’s evolving race.
obedience to his father – though to that also – he sacrificed his personal rights as the elect of the King and the assembly and fourteen of the best years of his life and went into exile in the forests. To his public spirit and his sense of public order (the great and supreme civic virtue in the eyes of the ancient Indians, Greeks, Romans, for at that time the maintenance of the ordered community, not the separate development and satisfaction of the individual was the pressing need of the human evolution) he sacrificed his own happiness and domestic life and the happiness of Sita. In that he was at one with the moral sense of all the antique races, though at variance with the later romantic individualistic sentimental morality of the modern man who can afford to have that less stern morality just because the ancients sacrificed the individual in order to make the world safe for the spirit of social order. Finally, it was Rama’s business to make the world safe for the ideal of the sattwic human being by destroying the sovereignty of Ravana, the Rākṣasa menace. All this he did with such a divine afflatus in his personality and action that his figure has been stamped for more than two millenniums on the mind of Indian culture, and what he stood for has dominated the reason and idealising mind of man in all countries – and in spite of the constant revolt of the human vital, is likely to continue to do so until a greater Ideal arises. And you say in spite of all these that he was no Avatar? If you like – but at any rate he stands among the few greatest of the great Vibhūtis. You may dethrone him now – for man is no longer satisfied with the sattwic ideal and is seeking for something more – but his work and meaning remain stamped on the past of the earth’s evolving race.