Sri Aurobindo
Letters of Sri Aurobindo
4. Reason, Science and Yoga
□ Hide link-numbers of differed places
 I have read Leonard Woolf’s article1, but I do not propose to deal with it in my comments on Professor Sorley’s letter – for apart from the ignorant denunciation and cheap satire in which it deals, there is nothing much in its statement of the case against spiritual thought or experience; its reasoning is superficial and springs from an entire misunderstanding of the case for the mystic. There are four main arguments he sets against it and none of them has
I have read Leonard Woolf’s article1, but I do not propose to deal with it in my comments on Professor Sorley’s letter – for apart from the ignorant denunciation and cheap satire in which it deals, there is nothing much in its statement of the case against spiritual thought or experience; its reasoning is superficial and springs from an entire misunderstanding of the case for the mystic. There are four main arguments he sets against it and none of them has any value.
any value.
Argument number one. Mysticism and mystics have always risen in times of decadence, of the ebb of life and their loud quacking is a symptom of the decadence. This argument is absolutely untrue. In the East the great spiritual movements have arisen in the full flood of a people’s life and culture or on a rising tide and they have themselves given a powerful impulse of expression and richness to its thought and Art and life; in Greece the mystics and the mysteries were there at the prehistoric beginning and in the middle (Pythagoras was one of the greatest of mystics) and not only in the ebb and decline; the mystic cults flourished
and richness to its thought and Art and life; in Greece the mystics and the mysteries were there at the prehistoric beginning and in the middle (Pythagoras was one of the greatest of mystics) and not only in the ebb and decline; the mystic cults flourished in Rome
in Rome when its culture was at high tide; many great spiritual personalities of Italy, France, Spain sprang up in a life that was rich, vivid and not in the least touched with decadence. This hasty and stupid
when its culture was at high tide; many great spiritual personalities of Italy, France, Spain sprang up in a life that was rich, vivid and not in the least touched with decadence. This hasty and stupid generalisation has no truth in it and therefore no value.
generalisation has no truth in it and therefore no value.
Argument number two. A spiritual experience cannot be taken as a truth (it is a chimera) unless it is proved just as the presence of a chair in the next room can be proved by showing it to the eye. Of course, a spiritual experience cannot be proved in that way, for it does not belong to the order of physical facts and is not physically visible or touchable. The writer’s proposition would amount to this that only what is or can easily be evident
would amount to this that only what is or can easily be evident to everybody without any need of training, development, equipment or personal discovery is to be taken as true. This is a position which, if accepted, would confine knowledge or truth within very narrow limits and get rid of a great deal of human culture. A spiritual peace – the peace
to everybody without any need of training, development, equipment or personal discovery is to be taken as true. This is a position which, if accepted, would confine knowledge or truth within very narrow limits and get rid of a great deal of human culture. A spiritual peace – the peace that passeth all understanding – is a common experience of the mystics all over the world, it is a fact but a spiritual fact, a fact of the invisible, and when
that passeth all understanding – is a common experience of the mystics all over the world, it is a fact but a spiritual fact, a fact of the invisible, and when
 one enters it or it enters into one, one knows that it is a
one enters it or it enters into one, one knows that it is a 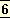
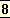
 truth of existence and is there all the time behind life and visible things. But how am I to prove these invisible facts to Mr. Leonard Woolf? He will turn away saying that this is the usual decadent quack-quack and pass contemptuously on – perhaps to write another cleverly shallow article on some subject of which he has no personal knowledge or experience.
truth of existence and is there all the time behind life and visible things. But how am I to prove these invisible facts to Mr. Leonard Woolf? He will turn away saying that this is the usual decadent quack-quack and pass contemptuously on – perhaps to write another cleverly shallow article on some subject of which he has no personal knowledge or experience.
Argument number three. The generalisations based on spiritual experience are irrational as well as unproven. Irrational in what way? Are they merely foolish and inconceivable or
 do they belong to a suprarational order of experience to which the ordinary intellectual canons do not apply because these are founded on phenomena as they appear to the external mind and sense and not to an inner realisation which surpasses these phenomena? That is the contention of the mystics and it cannot be dismissed by merely saying that as these generalisations
do they belong to a suprarational order of experience to which the ordinary intellectual canons do not apply because these are founded on phenomena as they appear to the external mind and sense and not to an inner realisation which surpasses these phenomena? That is the contention of the mystics and it cannot be dismissed by merely saying that as these generalisations
 do not agree with the ordinary
do not agree with the ordinary
 experience, therefore they are nonsense and false. I do
experience, therefore they are nonsense and false. I do
 not undertake to defend all
not undertake to defend all
 that Joad or Radhakrishnan may have written – such as the statement
that Joad or Radhakrishnan may have written – such as the statement
 that the “universe is good” – but I cannot admit about many of these
that the “universe is good” – but I cannot admit about many of these
 statements condemned
statements condemned
 by the writer that they are
by the writer that they are
 irrational at all. “Integrating the personality” may have no meaning to him, it has a very clear meaning to me
irrational at all. “Integrating the personality” may have no meaning to him, it has a very clear meaning to me
 , for it is a truth of experience – and, if modern psychology is to be believed, it is not irrational, since there is in our being not only a conscious but an unconscious or subconscious or concealed subliminal part and it is not impossible to become aware of both and make some kind of integration. To transcend both also may have
, for it is a truth of experience – and, if modern psychology is to be believed, it is not irrational, since there is in our being not only a conscious but an unconscious or subconscious or concealed subliminal part and it is not impossible to become aware of both and make some kind of integration. To transcend both also may have
 a rational meaning if we admit that as there is a subconscious so there may be a superconscious part of our being; to reconcile disparate parts of our nature or our experience
a rational meaning if we admit that as there is a subconscious so there may be a superconscious part of our being; to reconcile disparate parts of our nature or our experience
 is also not such a ridiculous or meaningless phrase. It is not absurd to say that the doctrine of Karma reconciles determinism and free-willism, since it
is also not such a ridiculous or meaningless phrase. It is not absurd to say that the doctrine of Karma reconciles determinism and free-willism, since it
 supposes that our own past action and therefore our past will determine
supposes that our own past action and therefore our past will determine
 to a great extent the present results, but not so as to exclude a present will modifying them and creating a fresh determinism of our existence yet to be. The phrase about the value of the world is quite intelligible when
to a great extent the present results, but not so as to exclude a present will modifying them and creating a fresh determinism of our existence yet to be. The phrase about the value of the world is quite intelligible when
 we see that it refers to a progressive value, not determined by the
we see that it refers to a progressive value, not determined by the 
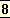
 good or bad experience of the moment, a value of existence developing through time and taken as a whole. As for the statement about God, it has no
good or bad experience of the moment, a value of existence developing through time and taken as a whole. As for the statement about God, it has no
 meaning if it is taken in connection with the superficial idea of the Divine current in popular religion, but it is a perfectly logical result of the premises
meaning if it is taken in connection with the superficial idea of the Divine current in popular religion, but it is a perfectly logical result of the premises
 that there is an Infinite and Eternal which is manifesting in itself Time and things that are phenomenally finite. One may accept or reject this complex idea of the Divine which is founded on co-ordination
that there is an Infinite and Eternal which is manifesting in itself Time and things that are phenomenally finite. One may accept or reject this complex idea of the Divine which is founded on co-ordination
 of the data of long spiritual experience passed through by thousands of seekers in all times, but I fail to see why it should be considered unreasonable. If it is because that means
of the data of long spiritual experience passed through by thousands of seekers in all times, but I fail to see why it should be considered unreasonable. If it is because that means
 “to have it not only in both ways but in every way”, I do not see why that
“to have it not only in both ways but in every way”, I do not see why that
 should be so reprehensible and inadmissible
should be so reprehensible and inadmissible
 . There can be after all a synthetic and global view and consciousness of things which is not bound by the oppositions and divisions of a mere
. There can be after all a synthetic and global view and consciousness of things which is not bound by the oppositions and divisions of a mere
 analytical and selective or dissecting intelligence.
analytical and selective or dissecting intelligence.
Argument number four. The plea of intuition is only a cover
 for the
for the
 inability to explain or establish by the use of reason – Joad and Radhakrishnan reason, but take refuge in intuition where
inability to explain or establish by the use of reason – Joad and Radhakrishnan reason, but take refuge in intuition where
 their reasoning fails. Can the issue be settled in so easy and trenchant a way? The fact is that the mystic depends
their reasoning fails. Can the issue be settled in so easy and trenchant a way? The fact is that the mystic depends
 on an inner knowledge, an inner experience; but if he philosophises, he must try to explain to the reason, though not necessary
on an inner knowledge, an inner experience; but if he philosophises, he must try to explain to the reason, though not necessary
 always by the reason
always by the reason
 alone, what he has seen to be the Truth. He cannot but say, “I am explaining a truth which is beyond outer phenomena and the intelligence which depends on phenomena; it really depends on
alone, what he has seen to be the Truth. He cannot but say, “I am explaining a truth which is beyond outer phenomena and the intelligence which depends on phenomena; it really depends on
 a certain kind of direct experience and the intuitive knowledge which arises from that experience, it
a certain kind of direct experience and the intuitive knowledge which arises from that experience, it
 cannot be adequately communicated by symbols appropriate to the world of outer phenomena, yet I am obliged to do as well as I can with these to help me towards some statement which will be intellectually acceptable to you.” There is no wickedness or deceitful cunning therefore in using metaphors and symbols with a cautionary “as it were”, as in
cannot be adequately communicated by symbols appropriate to the world of outer phenomena, yet I am obliged to do as well as I can with these to help me towards some statement which will be intellectually acceptable to you.” There is no wickedness or deceitful cunning therefore in using metaphors and symbols with a cautionary “as it were”, as in
 the simile of the focus, which is surely not intended as an argument but as a suggestive image. I may observe in passing
the simile of the focus, which is surely not intended as an argument but as a suggestive image. I may observe in passing
 that the writer himself takes refuge in metaphor frequently
that the writer himself takes refuge in metaphor frequently
 , beginning with the quack-quack
, beginning with the quack-quack
 and Joad
and Joad
 might well reply that he does so in order to damn the opposite
might well reply that he does so in order to damn the opposite 
 side, while avoiding the necessity of a sound philosophical reply to the philosophy
side, while avoiding the necessity of a sound philosophical reply to the philosophy
 he dislikes and repudiates. An intensity of belief is not the measure of truth, but neither is an intensity of unbelief the right measure.
he dislikes and repudiates. An intensity of belief is not the measure of truth, but neither is an intensity of unbelief the right measure.
As to the real nature of intuition and its relation to the intellectual mind, that is quite another and very large and complex question which I cannot deal with here
 . I have confined myself to pointing out that this article is quite
. I have confined myself to pointing out that this article is quite
 inadequate and superficial criticism. A case can be made against spiritual experience and spiritual philosophy and its positions, but to deserve a serious reply it must be put forward by a better advocate and
inadequate and superficial criticism. A case can be made against spiritual experience and spiritual philosophy and its positions, but to deserve a serious reply it must be put forward by a better advocate and
 it must touch the real centre of the problem, which lies here. As there is a category of facts to which our senses are our best available but very imperfect guides
it must touch the real centre of the problem, which lies here. As there is a category of facts to which our senses are our best available but very imperfect guides
 , as there is a category of truths which we seek by the keen but still imperfect light of our reason, so according to the mystic, there is a category of more subtle truths which surpass the reach both of the senses and the reason but can be ascertained by an inner direct knowledge and direct experience. These truths are supersensuous, but not the less real for that: they have immense results upon the consciousness changing its substance and movement, bringing especially deep peace and abiding joy, a great light of vision and knowledge, a possibility of the overcoming of the lower animal nature, vistas of a spiritual self-development which without them do not exist. A new outlook on things arises which brings with it, if fully pursued into its consequences, a great liberation, inner harmony, unification – many other possibilities besides. These things have been experienced, it is true, by a small minority of the human race, but still there has been a host of independent witnesses to them in all times, climes and conditions and numbered among them are some of the greatest intelligences of the past, some of the world’s most remarkable figures. Must these possibilities be immediately condemned as chimeras because they are not only beyond the average man in the street but also not easily seizable even by many cultivated intellects or because their method is more difficult than that of the ordinary sense or reason? If there is any truth in them, is not this possibility opened by them worth pursuing as disclosing
, as there is a category of truths which we seek by the keen but still imperfect light of our reason, so according to the mystic, there is a category of more subtle truths which surpass the reach both of the senses and the reason but can be ascertained by an inner direct knowledge and direct experience. These truths are supersensuous, but not the less real for that: they have immense results upon the consciousness changing its substance and movement, bringing especially deep peace and abiding joy, a great light of vision and knowledge, a possibility of the overcoming of the lower animal nature, vistas of a spiritual self-development which without them do not exist. A new outlook on things arises which brings with it, if fully pursued into its consequences, a great liberation, inner harmony, unification – many other possibilities besides. These things have been experienced, it is true, by a small minority of the human race, but still there has been a host of independent witnesses to them in all times, climes and conditions and numbered among them are some of the greatest intelligences of the past, some of the world’s most remarkable figures. Must these possibilities be immediately condemned as chimeras because they are not only beyond the average man in the street but also not easily seizable even by many cultivated intellects or because their method is more difficult than that of the ordinary sense or reason? If there is any truth in them, is not this possibility opened by them worth pursuing as disclosing
 a highest range of
a highest range of
 self-discovery and world
self-discovery and world 
 discovery by the human soul? At its best, taken as true, it must be that – at its lowest taken as only a possibility, as all things attained by man have been only a possibility in their earlier stages, it is a great and may well be a most fruitful adventure.
discovery by the human soul? At its best, taken as true, it must be that – at its lowest taken as only a possibility, as all things attained by man have been only a possibility in their earlier stages, it is a great and may well be a most fruitful adventure.
Current publication:
Sri Aurobindo. Letters on Yoga // SABCL.- Volume 22. (≈ 28 vol. of CWSA).- Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 1971.- 502 p.
Other publications:
Sri Aurobindo. Letters on Yoga. I // CWSA.- Volume 28. (≈ 22 vol. of SABCL).- Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 2012.- 590 p.
[Largest or earliest found passage: ] Sri Aurobindo. Letters of Sri Aurobindo: In 4 Series.- First Series [On Yoga].- Bombay: Sri Aurobindo Sircle, 1947.- 416 p.
 I have read Leonard Woolf’s article1, but I do not propose to deal with it in my comments on Professor Sorley’s letter – for apart from the ignorant denunciation and cheap satire in which it deals, there is nothing much in its statement of the case against spiritual thought or experience; its reasoning is superficial and springs from an entire misunderstanding of the case for the mystic. There are four main arguments he sets against it and none of them has
I have read Leonard Woolf’s article1, but I do not propose to deal with it in my comments on Professor Sorley’s letter – for apart from the ignorant denunciation and cheap satire in which it deals, there is nothing much in its statement of the case against spiritual thought or experience; its reasoning is superficial and springs from an entire misunderstanding of the case for the mystic. There are four main arguments he sets against it and none of them has